
Click on the FREQUENCY SWEEP button to begin the scan.Switch to the frequency analysis tab and set the following parameters:.

Click the "Calculate Modes" button and then, select the mode of interest (mode #1) in the Mode list.Press on the MESH STRUCTURE button to plot the meshed structure. To open the eigenmode solver analysis window. This will place the eigensolver region at the input bus for the ring resonator. Set the properties according to the following table. Press on the arrow on the on the SIMULATION buttonĪnd select the EIGENSOLVER from the pull-down menu.The coupling length and radius used for the first part of the simulation are just an initial guess and will be modified to the correct values later.Īdd eigenmode solver and find group index Set the properties of the ring resonator according to the following table.Select RING RESONATOR from the list and press the INSERT button.This will open the object library window. Press on arrow on the COMPONENTS buttonĪnd select INTEGRATED OPTICS from the pull-down menu.Set the properties of the insulator substrate rectangle according to the following table. Press on arrow on the STRUCTURES buttonĪnd select a RECTANGLE from the pull-down menu.You can save the MODE Simulation Project file (.lms) at any point in this process. The fifth section shows how to compare the propagator results with analytical and 3D FDTD results. The fourth and sixth sections discuss how to set up the propagator simulation. Section 2 and section 3 use the eigenmode solver and the analytical results from the discussion and results section to design the ring resonator. lms file and proceed to the following steps if you want to know the results first. You can skip this step, open the associated.
The first section describes how to setup the model. Compare results with the theoretical design and 3D FDTD results.Use the Eigenmode Solver to choose the waveguide spacing, coupling length and ring length for the desired FSR and Q factor.Insert a ring resonator object from the components library.In this example, we show how MODE can be used to design a ring resonator. Part 3: Final parameter extraction using FDTD Learning objectives
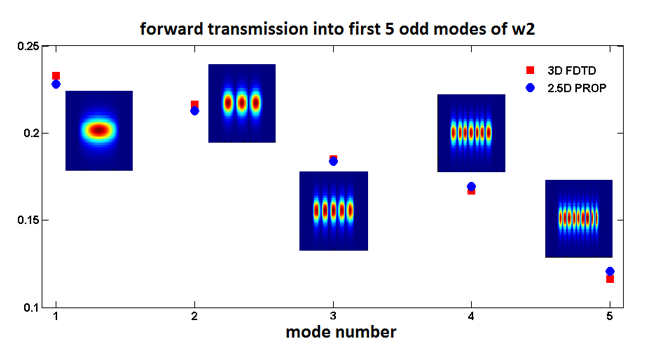
Part 2: Parameter extraction and Monte Carlo using MODE Part 1: Design and initial simulation using MODE Part 3 does the final simulation and parameter extraction using a 3D FDTD simulation. In Part 2, we will consider how to carry out the parameter extraction and Monte Carlo analysis process for this design. Free spectral range (FSR) and quality factor (Q factor) are key performance metrics for this silicon on insulator (SOI) based waveguide design targeting on-chip communication applications. Part 1 of the ring resonator tutorial uses MODE to design and simulate a ring resonator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
